
In the wide range of microscopes available, quite a few have different applications. While you may expect most microscope models to display close-up microscopic images, some can translate those images into other forms.
The thermal imaging microscope is one such example. A thermal imaging microscope is a type of microscope that uses infrared radiation, producing a high-resolution image with thermal properties. This is especially useful if you’re seeking the thermal properties of a microscopic sample.
There are several uses for thermal imaging microscopes and what they can measure from a collected sample. You can use it for scientific and medicinal applications. Let’s explain how a thermal imaging microscope works and its typical uses.
Contents
How Does a Thermal Imaging Microscope Work?
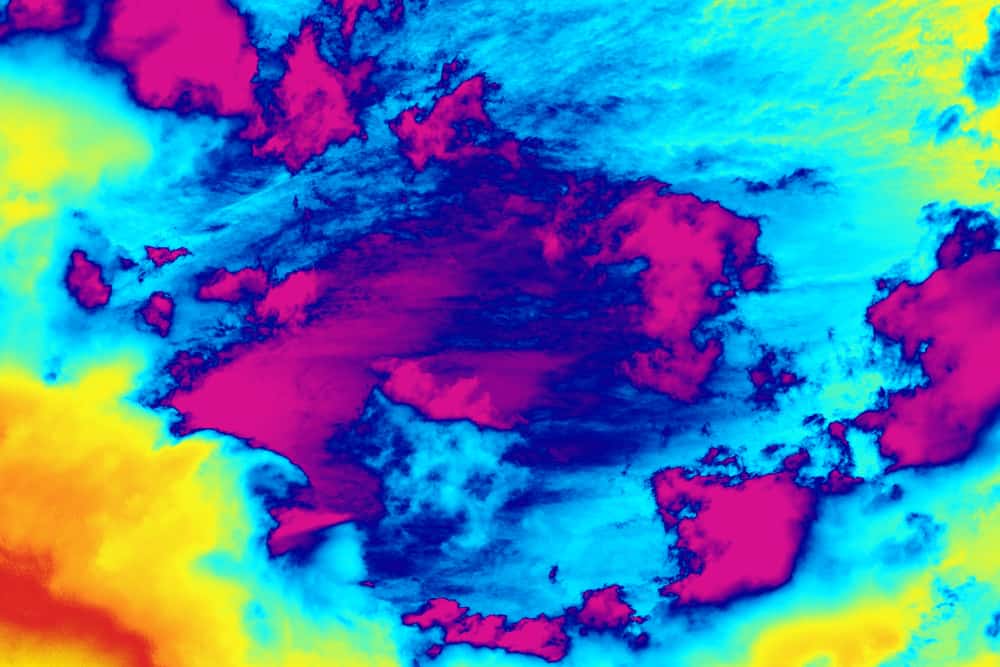
If you’ve ever used thermal technology before, then how a thermal imaging microscope works is relatively straightforward. For this microscope to create thermal images, a thermal detector measures the infrared radiation emitted by the sample.
Thermal detection is related to the sample’s temperature, so you must ensure the sample is at the preferred temperature and kept in a temperature-controlled environment.
The thermal information is then scanned to create an image representing the sample’s temperature distribution. You may recognize it in other applications, like weather temperature maps and thermal body scan imaging. Depending on the temperature reading, your microscopic image will appear in red, yellow, blue, and purple shades.
If your sample often changes temperature, this may be something to note for your studies. A sample may require multiple scans to measure its temperature at different times. A thermal imaging microscope can be helpful because it can gather data that a non-thermal microscope can’t show.
Why Are Thermal Imaging Microscopes Useful?
Thermal imaging microscopes are particularly useful for studying any material with different temperature or thermal conductivity variations. Some of these materials can include electronic components, polymers, and composites, to name a few.
A thermal imaging microscope provides more detailed information about the thermal properties of a sample than a typical microscope. With it, you can determine the sample’s location and the magnitude of temperature gradients. This can be critical information to know, especially when trying to understand the behavior and performance of these materials.
Common Applications for Thermal Imaging Microscopes
There are several common uses for thermal imaging microscopes in the scientific field. Different materials may require thermal scanning to determine their average temperature reading, location, and behavior.
Analyzing Electronic Devices
One application of thermal imaging microscopes is in the analysis of electronic devices. This is one application in which temperature is critical in determining the device’s performance and reliability.
On a microscopic level, you can determine a small electronic device’s properties when placed under pressure. A thermal imaging microscope can identify hot spots or areas of thermal stress in an electronic device, which you can address to prevent damage or failure.
Analyzing Polymers and Composites
Another application of thermal imaging microscopes is in the analysis of polymers and composites, where temperature can be a critical factor in determining the material’s mechanical properties. By using a thermal imaging microscope, researchers can visualize the material’s thermal properties and better understand how temperature affects its mechanical behavior.
Benefits of Using a Thermal Imaging Microscope
Besides its obvious benefits, there are several reasons why a thermal imaging microscope can be useful in the field.
Provides Non-Destructive Analysis
Thermal imaging microscopes provide a non-destructive analysis of materials, meaning you can use them to study samples without damaging or altering them. This can be especially useful for analyzing delicate or valuable material, such as electronic components or historical artifacts. To measure the temperature of an ancient artifact, for instance, you would only need a small sample of it under a microscope to gather this data, thanks to a thermal imaging microscope.
Provides High Spatial Resolution
Thermal imaging microscopes provide high spatial resolution images showing a material’s thermal properties. A high-resolution microscopic image gives enough information for researchers to see small details that are otherwise not visible with other types of image scans.
This is particularly useful for studying materials with complex thermal properties or small-scale features like electronic components or microstructures. For instance, a high-quality thermal scan of an electronic device can show you the device’s overall temperature, but with a thermal imaging microscope, you can see details in the device up close that may otherwise be missed.
Quantitative Analysis
A thermal imaging microscope can also provide a quantitative analysis of thermal properties. This can include thermal conductivity, heat capacity, and thermal expansion. With this analysis, researchers can obtain detailed information about the thermal behavior of materials, how it changes under different conditions, and their overall temperature.
Offers Real-Time Monitoring of Thermal Imaging
While obtaining a single image from a thermal imaging microscope can be helpful, this microscope can also be used for real-time monitoring of thermal processes. A thermal imaging microscope can record a specimen over time, providing a complete picture for researchers to observe and analyze the specimen’s temperature changes and thermal behavior.
This can be particularly useful for studying dynamic processes, such as chemical reactions that can only be seen on a microscopic level, phase transitions, and mechanical deformation.
Versatility in its Applications
Thermal imaging microscopes can be used for a wide range of applications in many different fields. Some applications include materials science, biology, medicine, and engineering. This makes them a versatile tool for scientific research across multiple fields.
Conclusion
A thermal imaging microscope can be a potent and valuable tool for research. To examine a material up-close with non-destructive analysis, a thermal imaging microscope can provide real-time monitoring of a specimen’s thermal properties, show its temperature distribution, and more. It is a tool that can be applied to numerous fields of materials science and engineering research, providing detailed information about a sample’s thermal properties and behavior.

