Asteroids: Cosmic Time Capsules of the Solar System
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Are Asteroids?
- Formation of Asteroids
- Asteroids and the Solar System
- Scientific Insights from Asteroids
- Asteroid Impacts on Earth
- Asteroids and Space Exploration
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Introduction
Asteroids, often perceived as mere space rocks, are in fact crucial to our understanding of the solar system’s history and evolution. These celestial bodies, remnants from the early solar system, act as cosmic time capsules, preserving information about the conditions and processes that prevailed over four billion years ago. By studying asteroids, scientists can glean insights into the formation of planets and the dynamic processes that have shaped our cosmic neighborhood.
Artist: Wikideas1
What Are Asteroids?
Asteroids are small, rocky objects that orbit the Sun, primarily found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. These bodies vary greatly in size, from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers in diameter. Unlike planets, asteroids do not have atmospheres, and their irregular shapes reflect their tumultuous pasts, marked by collisions and gravitational interactions.
Artist: Theresa knott at English Wikibooks
Formation of Asteroids
The formation of asteroids dates back to the early solar system, approximately 4.6 billion years ago. During this period, the solar nebula—a rotating disk of gas and dust—began to coalesce under gravity, forming the Sun and the planets. However, not all material was incorporated into these larger bodies. Some remained as smaller fragments, which eventually became asteroids.
These remnants are composed of primordial materials, offering a pristine glimpse into the solar system’s formative years. The study of asteroid composition, through spectroscopy and sample-return missions, provides critical data on the building blocks of planets.
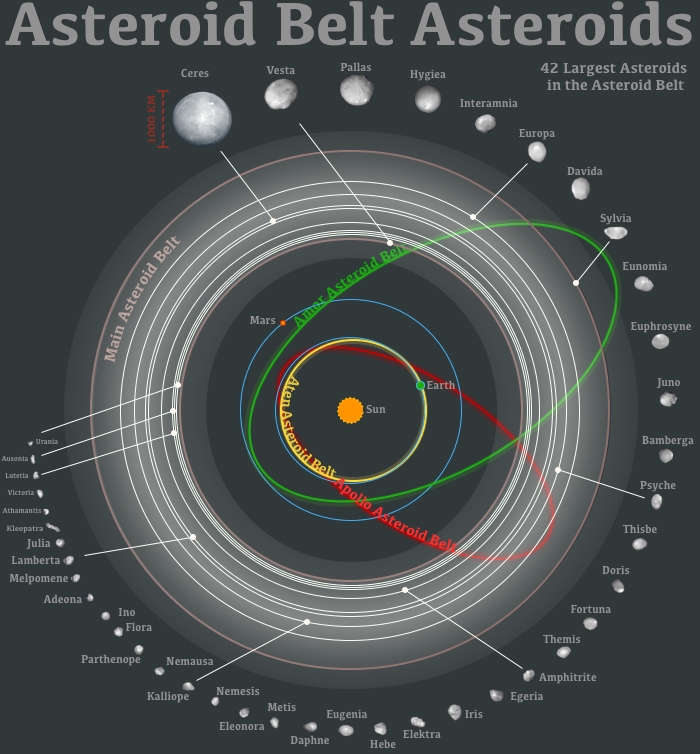
Asteroids and the Solar System
Asteroids play a significant role in the solar system’s architecture and evolution. Their distribution and movement are influenced by gravitational interactions with planets, particularly Jupiter, which can alter their orbits and lead to collisions. These interactions have implications for planetary formation theories and the distribution of materials across the solar system.
Moreover, asteroids are thought to have delivered water and organic compounds to the early Earth, potentially contributing to the emergence of life. This hypothesis underscores the importance of asteroids in understanding planetary habitability and the origins of life.
Scientific Insights from Asteroids
Asteroids provide a wealth of scientific information that can enhance our understanding of the solar system. By analyzing their composition, scientists can infer the conditions of the early solar system. For instance, carbonaceous chondrites, a type of asteroid, contain water and organic molecules, offering clues about the distribution of these essential ingredients in the early solar system.

Artist: NASA/Goddard/University of Arizona
Additionally, the study of asteroid orbits and collisions contributes to our knowledge of celestial mechanics and the dynamic processes that shape planetary systems. These insights are crucial for developing models of solar system evolution and predicting future changes.
Asteroid Impacts on Earth
Asteroid impacts have played a pivotal role in Earth’s geological and biological history. The most famous impact, which occurred approximately 66 million years ago, is believed to have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs. This event, known as the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction, highlights the potential for asteroids to dramatically alter life on Earth.

Artist: O.V.E.R.V.I.E.W.
Understanding the frequency and consequences of asteroid impacts is essential for assessing planetary defense strategies. Current efforts focus on tracking near-Earth objects (NEOs) and developing technologies to mitigate potential threats.
Asteroids and Space Exploration
Asteroids are prime targets for space exploration due to their scientific value and potential for resource utilization. Missions like NASA’s OSIRIS-REx and Japan’s Hayabusa2 have successfully collected samples from asteroids, providing direct access to ancient materials that can be analyzed in laboratories on Earth.

Note: used in NASA SP-349 ‘Pioneer Odyssey – Encounter with a Giant’ fig. 1-24 and SP-446 ‘Pioneer – First to Jupiter, Saturn, and Beyond’ fig 1-24
(Uploader’s note: Image has been losslessly cropped from source, with no color correction.)
Artist: Rick Guidice
Future missions aim to explore asteroid mining, which could provide resources such as metals and water for space exploration and colonization efforts. These endeavors underscore the dual role of asteroids as both scientific treasures and potential stepping stones for humanity’s expansion into the solar system.
FAQ
What is the difference between asteroids and comets?
Asteroids and comets are both small celestial bodies, but they differ in composition. Asteroids are primarily composed of rock and metal, while comets contain significant amounts of ice and dust. Comets often exhibit visible atmospheres and tails when they approach the Sun, due to the sublimation of their icy components.
How do scientists study asteroids?
Scientists study asteroids through a combination of telescopic observations, spacecraft missions, and laboratory analysis of meteorites. Telescopes can determine asteroid orbits and compositions, while spacecraft missions provide detailed data and samples. Meteorites, which are fragments of asteroids that have fallen to Earth, offer direct insights into their composition and history.

Artist: Lance, NASA
Conclusion
Asteroids are more than just space debris; they are vital to understanding the history and evolution of our solar system. As cosmic time capsules, they preserve the conditions of the early solar system and offer insights into planetary formation and the origins of life. With ongoing and future missions, asteroids will continue to illuminate the mysteries of our cosmic past and potentially pave the way for humanity’s future in space. To delve deeper into the fascinating world of asteroids, consider exploring related topics and staying updated with the latest space exploration missions.
